The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) is the foundational document of international human rights law. Following the atrocities of World War II, the international community vowed to prevent such grave human rights abuses from occurring in the future. To do this it created the UDHR, which contains thirty articles related to important civil, economic, social, cultural, and political rights.
-
Article 1: Right to Equality, Dignity, and Respect
Article 2: Freedom from Discrimination
Article 3: Right to Life, Freedom, and Safety
Article 4: Freedom from Slavery or Servitude
Article 5: Freedom from Torture or Cruel, Degrading, or Inhuman Treatment
Article 6: Right to Personhood Before the Law
Article 7: Right to Equality Before the Law
Article 8: Right to Seek Justice and Remedy
Article 9: Freedom from Arbitrary Arrest and Imprisonment
Article 10: Right to a Fair and Public Trial
Article 11: Right to Presumption of Innocence
Article 12: Right to Privacy
Article 13: Freedom of Movement
Article 14: Right to Asylum
Article 15: Right to Nationality
Article 16: Right to Marry and Start a Family
Article 17: Right to Own Property
Article 18: Freedom of Thought, Religion, and Belief
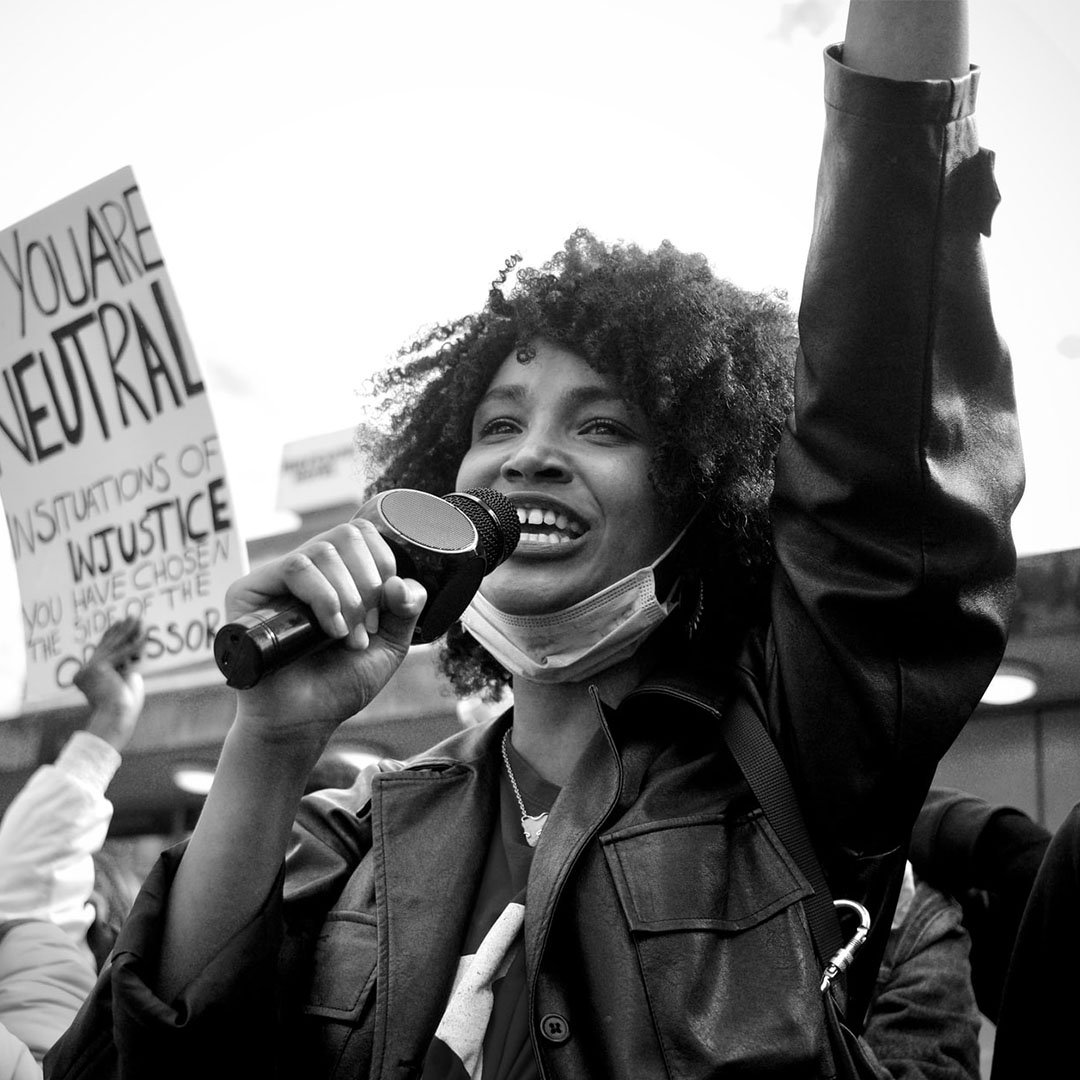
Article 19: Freedom of Opinion and Expression
Article 20: Freedom of Assembly and Association
Article 21: Right to Participate in Government
Article 22: Right to Social Security
Article 23: Right to Work and Join a Union
Article 24: Right to Rest and Leisure
Article 25: Right to an Adequate Standard of Living
Article 26: Right to Education
Article 27: Right to Participate in Cultural, Artistic, and Scientific Life
Article 28: Right to a Free and Fair World
Article 29: Our Duty to Each Other
Article 30: Human Rights Belong to You